A variable cost is any corporate expense that changes along with changes in production volume. As production increases, these costs rise and as production decreases, they fall. Common examples include raw materials, direct labor, and packaging. While variable costs are generally thought of as physical items, such as raw materials, variable costs include all expenses which increase incrementally with each additional unit produced. Sales commissions, for example, are also considered variable because the size of a commission is tied to the volume of products sold by an employee. A myriad of factors influence variable costs. Understanding these factors can help businesses strategize better and maintain optimal operations. In industries where production is labor-intensive, hiring more workers during peak periods can lead to higher direct labor costs. On the other hand, when there's a decline in demand, production might decrease, leading to a reduction in variable costs as fewer resources are consumed. However, it's important to note that variable costs do not always rise or fall in a perfectly linear fashion. There might be instances where economies of scale come into play, affecting the proportionality of these costs. The cost per unit is the amount it takes to produce a single item. This can fluctuate based on various factors such as the price of raw materials or changes in labor costs. For example, if a spike in demand for a particular raw material occurs due to global shortages, the cost to purchase that material will increase. This, in turn, will raise the cost per unit, leading to higher variable costs for businesses reliant on that material. Alternatively, advancements in technology or improved procurement strategies might lower the cost per unit, resulting in reduced variable costs. Regularly monitoring and adjusting to these shifts is crucial for maintaining profitability. Economies of scale refer to the cost advantage that companies achieve when production becomes efficient, leading to a reduction in the cost per unit as production volume increases. For instance, purchasing raw materials in bulk might result in discounts, thereby reducing the cost per unit. Similarly, streamlining production processes can also lead to decreased costs per item. However, it's essential to recognize that economies of scale can plateau. After reaching a certain production level, the benefits might diminish, and variable costs may not decrease at the same rate. Because Variable Costs are tied to production, they are usually thought of as a constant amount expensed per unit produced. For example, if a lemonade manufacturer increases production from 100,000 bottles a week to 250,000, the cost per bottle remains the same, but the total variable cost increases proportionately to the increase in production volume. To determine total variable cost, simply multiply the cost per unit with the number of units produced. It's worth mentioning that firms may reduce the cost per unit by benefiting from Economies of Scale, which allows for decreased variable costs due to increased efficiency and bargaining power from higher volume. Variable costs stand in contrast with fixed costs since fixed costs do not change directly based on production volume. Examples of fixed costs are employee wages, building costs, and insurance. Between variable and fixed costs are semi-variable costs (also known as semi-fixed or mixed costs). These costs have a mix of costs tied to each unit of production and a fixed cost which will be incurred regardless of production volume. For example, the cost of deliveries includes the fixed costs of insurance, depreciation, and loan payments on a fleet of delivery vehicles, but the cost of gasoline is variable depending on the number of deliveries. An increase in the number of deliveries being made will increase the expense of gasoline, but not the cost of the insurance, depreciation, or loans. Implementing knowledge of variable costs can lead to improved decision-making and better business strategies. Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) analysis is a financial tool that businesses use to determine how changes in costs and sales volume can affect profits. Through CVP analysis, companies can identify the break-even point—the level of sales at which total revenues equal total costs. Knowing this point can help businesses set sales targets, plan production volumes, and strategize pricing. Moreover, understanding how changes in variable costs can impact profitability allows companies to make informed decisions about scaling up or down. For businesses, setting the right price for products or services is a balancing act. With a thorough understanding of variable costs, companies can set prices that cover these costs and also account for fixed costs, ensuring profitability. By analyzing variable costs, businesses can also identify opportunities for discounts, promotions, or premium pricing, depending on market dynamics and cost structures. Variable costs can guide businesses in determining how to allocate resources optimally. For instance, if a particular product has a high variable cost but generates low revenue, it might be more beneficial to divert resources to another product with a better profit margin. By constantly evaluating and adjusting resource allocation based on variable cost data, businesses can ensure they're operating efficiently and maximizing returns. While understanding variable costs is vital, it's equally essential to be aware of their limitations. One of the primary limitations of variable costs is the difficulty in predicting sudden shifts. For instance, sudden spikes in raw material prices or unforeseen changes in labor costs can significantly impact the variable costs of a business, affecting profitability. Focusing solely on variable costs might lead businesses to overlook longer-term strategic considerations. Cutting costs by sourcing lower-quality raw materials can reduce variable costs in the short term but might harm the brand's reputation and customer trust in the long run. Determining what constitutes a direct variable cost can sometimes be challenging. Electricity used in a production process might increase with production volume, but it's hard to attribute a specific amount to each unit produced. Such complexities can sometimes obscure the true variable costs, leading to misinformed decisions. Efficient management of variable costs is a cornerstone of successful business operations. Lean management focuses on eliminating waste in all forms from the production process. This might mean reducing idle time, optimizing the use of raw materials, or improving production workflows. By embracing lean techniques, businesses can effectively reduce their variable costs and improve overall efficiency. One direct approach to manage variable costs is through negotiations with suppliers. By securing better deals, longer credit terms, or bulk purchase discounts, companies can achieve significant reductions in their material costs, which constitute a large part of variable costs for many businesses. Refining and optimizing production processes can lead to reduced waste, faster production times, and ultimately, lower variable costs. This might involve training employees, investing in advanced machinery, or adopting new production techniques. Sometimes, replacing a high-cost material with a more affordable alternative without compromising on quality can lead to substantial savings. Material substitution, when done right, can be a strategic move to manage variable costs effectively. Variable costs are the expenses that change in direct proportion to the volume of goods or services a company produces. These costs, which change with production volume, encompass a wide range of expenses beyond just physical items. Factors like production volume, cost per unit, and economies of scale influence variable costs, impacting profitability. By understanding variable costs, businesses can conduct cost-volume-profit analysis, optimize pricing strategies, and allocate resources efficiently. However, variable costs have limitations, such as their unpredictability during sudden changes and potential neglect of long-term effects. Effective management involves implementing lean techniques, negotiating with suppliers, optimizing processes, and considering material substitution. Balancing these strategies while addressing complexities in cost identification ensures businesses make informed choices, optimizing their performance and sustaining success.Variable Costs Definition
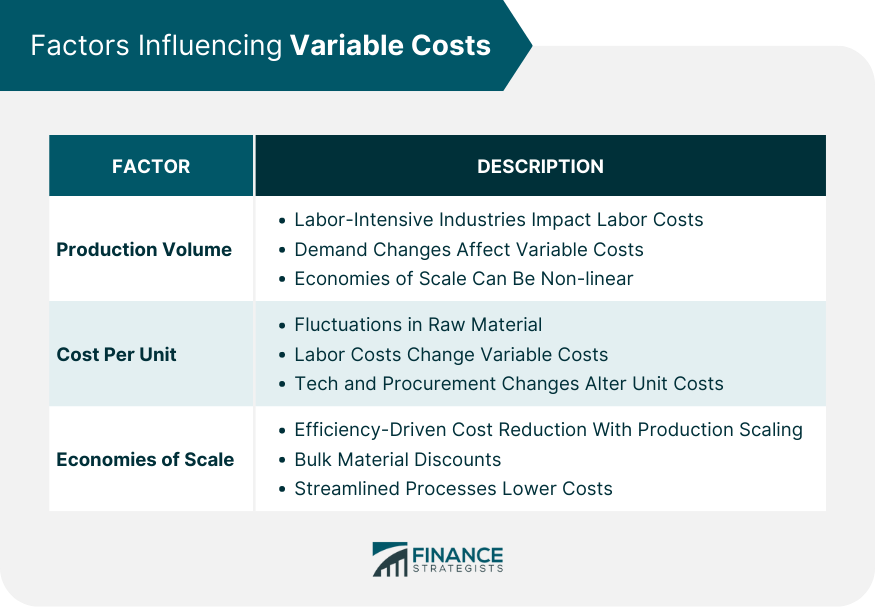
Factors Influencing Variable Costs
Production Volume
Cost Per Unit
Economies of Scale
How to Find Variable Cost

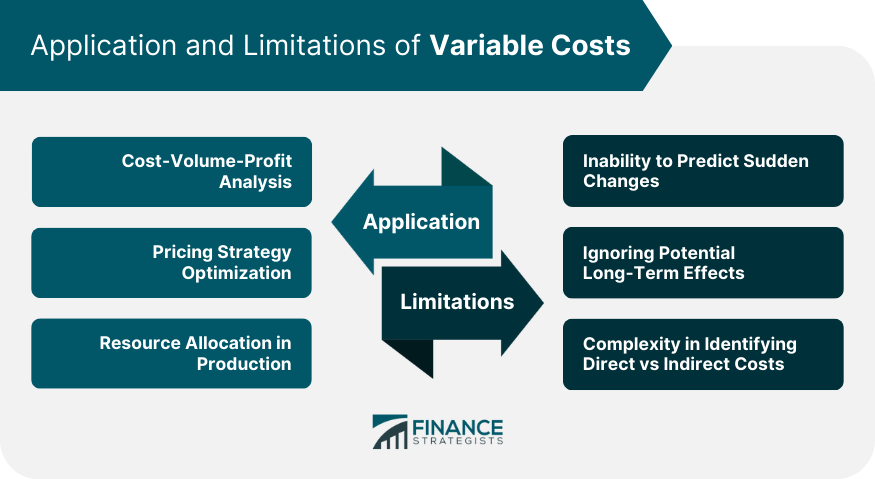
Application of Variable Costs
Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis
Pricing Strategy Optimization
Resource Allocation in Production
Limitations of Variable Costs
Inability to Predict Sudden Changes
Ignoring Potential Long-Term Effects
Complexity in Identifying Cost Types
Managing Variable Costs
Lean Management Techniques
Supplier Negotiations
Process Optimization
Material Substitution

Conclusion
Variable Cost FAQs
A variable cost is any corporate expense that changes along with changes in production volume.
To determine the total variable cost, simply multiply the cost per unit with the number of units produced.
If a lemonade manufacturer increases production from 100,000 bottles a week to 250,000, the cost per bottle remains the same, but the total variable cost increases proportionately to the increase in production volume.
Because variable costs are tied to production, they are usually thought of as a constant amount of expense per unit produced.
Variable costs stand in contrast with fixed costs, since fixed costs do not change directly based on production volume. Between variable and fixed costs are semi-variable costs (also known as semi-fixed or mixed costs).
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.













