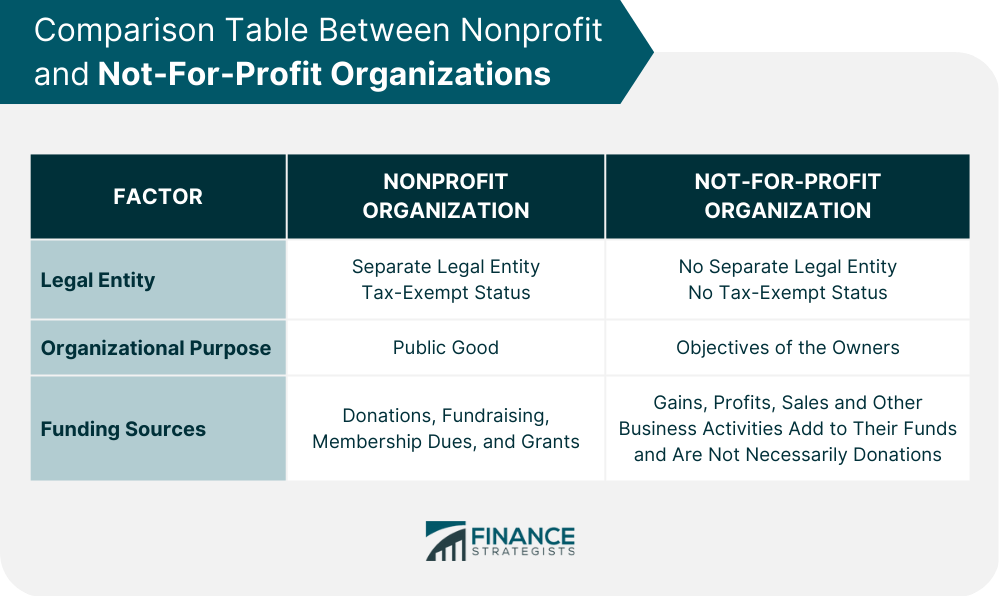
Nonprofit and not-for-profit organizations are two different types of entities that are often used interchangeably. Both types of organizations are organized for the purpose of serving a public good, but they differ in their legal structure, funding sources, and management practices. A nonprofit organization is a type of entity that is established for a public or charitable purpose. It is structured in such a way that its profits and assets are not distributed to its owners but rather are used to support its stated mission. It may be created for a variety of reasons, including advancing education, promoting the arts, or providing humanitarian aid. Further, nonprofits can be created by individuals, groups, or corporations, and they can take various legal forms, such as charitable trusts, foundations, or associations. A not-for-profit organization is similar to a nonprofit in that it is established for a public or charitable purpose. However, they are structured to serve the objectives of their owners rather than the public good. They may be created to further a specific cause or to provide a specific service to a particular community. Not-for-profits may be established by individuals or groups, and they can take various legal forms, such as cooperatives or social clubs. Nonprofit and not-for-profit organizations are distinct legal entities with different requirements and tax benefits. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) distinguishes between these two types of organizations based on the purpose of their formation and the ways in which they generate and use their funds. The IRS defines a nonprofit organization as an entity that is organized and operated exclusively for religious, charitable, scientific, testing for public safety, literary, or other specified purposes. In order to qualify as a nonprofit, an organization must meet certain requirements, such as having a specific organizational purpose, operating in a non-partisan manner, and limiting the compensation of its officers and directors. Not-for-profit organizations, on the other hand, are entities that are established for a specific purpose or to serve a particular community rather than for the benefit of their owners. While they may generate revenue, any profits are typically reinvested back into the organization rather than being distributed to the owners. Not-for-profit organizations are not eligible for tax-exempt status like nonprofit organizations but may still receive some tax benefits depending on their legal structure and activities. They are subject to some regulatory requirements, but not to the same extent as nonprofit organizations. The organizational structure of nonprofit and not-for-profit organizations differ based on their legal form and the nature of their mission. Generally, both types of organizations are governed by a board of directors, which is responsible for setting policies and overseeing the operations of the organization. Nonprofit organizations have the option to organize themselves in various ways, such as an unincorporated association, trust, corporation, or limited liability company. However, the IRS only recognizes LLCs as nonprofit 501(c)(3) if all members are 501(c)(3) organizations. While a corporation typically offers the most advantages, a trust or association may be more appropriate for certain situations. Not-for-profit organizations are typically run by volunteers who are passionate about the mission of the organization. They may have a less formal organizational structure and may rely on the personal relationships and networks of their members to achieve their goals. Nonprofit organizations rely heavily on donations from individuals, corporations, and foundations to support their operations. Donations can be solicited through various channels, such as direct mail campaigns, fundraising events, and online donation platforms. Nonprofit organizations also often have ongoing donation campaigns or partnerships with businesses and other organizations to generate recurring donations. In addition to donations, nonprofit organizations may also receive grants from government agencies, charitable foundations, or other funding sources. Grants may be given for specific programs or projects or may be unrestricted funds that can be used for general organizational expenses. In contrast, not-for-profit organizations may generate revenue through membership fees or sales of products or services related to their mission or purpose. This may include admission fees to events or programs, sales of merchandise, or fees for educational or training programs. Such organizations may also receive donations from individuals or corporations, but it is not their primary funding source. It is worth noting that both nonprofit and not-for-profit organizations may face challenges in securing funding and generating revenue, particularly during times of economic uncertainty or changes in donor or member behavior. Many organizations may need to develop innovative strategies for fundraising and revenue generation, such as crowdfunding campaigns, social media outreach, or grant writing workshops. Additionally, some organizations may need to diversify their funding sources or explore new revenue streams to ensure long-term sustainability. The following table summarizes some of the key differences between nonprofit and not-for-profit organizations: There are many examples of nonprofit and not-for-profit organizations that exist around the world. Some examples of nonprofit organizations include the American Red Cross, Doctors Without Borders, and the Make-A-Wish Foundation. These organizations are dedicated to serving the public good and rely on donations from individuals and corporations to fund their activities. Not-for-profit organizations concentrate on specific activities within the community or society, such as religion, education, science, and public safety. They tend to focus on smaller groups and can include clubs, trade organizations, religious groups, welfare societies, and similar entities. Among the example organizations include Girl Scouts of America and professional associations like the American Bar Association. These organizations are typically focused on serving the interests of their members or a specific community rather than the broader public. Deciding between setting up a nonprofit or not-for-profit organization can be a complex decision. There are many factors that should be considered, including the purpose of the organization, the availability of funding, and the management structure. If the primary goal of the organization is to serve the public good, a nonprofit organization may be the best choice. Nonprofits are eligible for tax-exempt status and can attract donations and grants from a wide range of sources. They also typically have a more formal organizational structure, which can help ensure that they are well-managed and effective in achieving their mission. On the other hand, if the primary goal of the organization is to serve the interests of a particular community or group, a not-for-profit organization may be the better choice. They are typically more flexible in their management structure and can be more responsive to the needs of their members or owners. They may also have access to funding sources that are not available to nonprofit organizations. Ultimately, the choice between setting up a nonprofit or not-for-profit organization will depend on the specific circumstances of the organization and the goals of its founders. Nonprofit and not-for-profit organizations are two distinct types of entities that are organized for the purpose of serving a public good. Nonprofit organizations are structured to benefit the broader community and are eligible for tax-exempt status and other regulatory benefits. Not-for-profit organizations are typically structured to serve the interests of a particular community or group and are not eligible for the same tax benefits. When deciding between setting up a nonprofit or not-for-profit organization, it is important to consider factors such as the purpose of the organization, its funding sources, and its management structure. Seeking the advice of a financial advisor or attorney can help ensure that the organization is structured in the most effective and efficient way possible.Nonprofit vs Not-For-Profit Organizations: Overview
Legal Distinctions Between Nonprofit and Not-For-Profit Organizations
Organizational Structure of Nonprofit and Not-For-Profit Organizations
Funding and Revenue Streams for Nonprofit and Not-For-Profit Organizations
Examples of Nonprofit and Not-For-Profit Organizations
Nonprofit vs Not For Profit: Which One Should You Set Up?
The Bottom Line
Nonprofit vs Not-For-Profit FAQs
A nonprofit organization is a type of entity that is established for a public or charitable purpose. It is structured in such a way that its profits and assets are not distributed to its owners but rather are used to support its stated mission.
A not-for-profit organization is an entity that is established to further the interests of its owners, rather than to benefit the public good. It may be created to further a specific cause or to provide a specific service to a particular community.
Both types of organizations are typically governed by a board of directors, which is responsible for setting policies and overseeing the operations of the organization. Nonprofit organizations may also have an executive director who is responsible for managing day-to-day operations.
Nonprofit organizations may generate revenue through donations from individuals, corporations, or foundations, as well as through grants from government agencies. Not-for-profit organizations may rely on membership fees, fundraising events, or other forms of income to support their operations.
The choice between setting up a nonprofit or not-for-profit organization will depend on the specific circumstances of the organization and the goals of its founders. It may be helpful to seek the advice of a financial advisor or attorney to help determine the best legal structure for the organization.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















