In a regressive tax system, the tax rate reduces as the taxpayer's income increases. For example, a sales tax on basic necessities such as food and clothing is an example of a regressive tax system. Low-income households allocate a greater proportion of their income towards necessities than high-income households, which leads to them paying a higher percentage of their income in sales taxes. In contrast, a progressive tax system increases the tax rate as the taxpayer's income increases. High-income households pay a higher percentage of their income in taxes than low-income households. For example, a graduated income tax is an example of a progressive tax system. The impact of a regressive tax system on low-income households is significant. A regressive tax system places a greater burden on low-income households, who are already struggling to make ends meet. Low-income households allocate a larger proportion of their income toward fundamental needs, such as food, housing, and healthcare. Therefore, a tax on necessities such as food and clothing would significantly impact low-income households. Furthermore, a regressive tax system can exacerbate income inequality. When low-income households pay a higher percentage of their income in taxes than high-income households, the gap between the rich and the poor widens. This widening gap can have a negative impact on social and economic stability. A sales tax is one of the most common examples of a regressive tax policy. Sales taxes are usually flat taxes that apply to all purchases, regardless of the buyer's income level. Low-income households allocate a larger percentage of their income towards essential items like food, clothing, and healthcare, resulting in them paying a greater proportion of their income in sales taxes. Another example of a regressive tax policy is a flat income tax rate. A flat income tax rate is a tax rate that is the same for all income levels. While a flat income tax rate may seem fair, it can disproportionately impact low-income households. Low-income households spend a higher percentage of their income on basic necessities, meaning they have less disposable income than high-income households. Therefore, a flat income tax rate can significantly impact low-income households. The impact of a regressive tax system on the economy is complex. On the one hand, a regressive tax system can generate revenue and finance public goods and services. On the other hand, a regressive tax system can exacerbate income inequality, reduce economic mobility, and slow economic growth. Low-income households, who pay a larger proportion of their income in taxes than high-income households, have a reduced amount of disposable income available for spending on goods and services. This consumer spending reduction can slow economic growth and reduce job creation. Additionally, when high taxes burden low-income households, they may be less likely to invest in education, training, and other forms of human capital development. This can reduce their ability to compete in the labor market and increase their reliance on public assistance programs. Furthermore, a regressive tax system can exacerbate income inequality and have adverse social and economic consequences. Income inequality can lead to social unrest, reduce social mobility, and reduce the overall economic growth of a country. Additionally, when low-income households do not have enough money to purchase basic necessities, they may rely on public assistance programs such as food stamps and Medicaid, which can increase government spending. A regressive tax system has received significant criticism for its impact on low-income households and the economy. The main criticism of a regressive tax system is its disproportionate burden on low-income households struggling to make ends meet. Low-income households pay a higher percentage of their income in taxes than high-income households, exacerbating income inequality and reducing social mobility. Another criticism of a regressive tax system is that it can reduce economic growth by reducing consumer spending. When low-income households have less disposable income to spend on goods and services, it can slow down economic growth and job creation. While a regressive tax system has received significant criticism, it also has some advantages. One of the main advantages of a regressive tax system is its simplicity. A regressive tax system is easier to administer and enforce than a progressive one. This is because a regressive tax system has a flat tax rate for all income levels, requiring fewer resources to implement and enforce. Additionally, a regressive tax system has lower administrative costs than a progressive tax system. A regressive tax system requires less paperwork and fewer resources to administer than a progressive tax system. This means it can be implemented at a lower cost to the government. Regressive tax policies are prevalent in many countries worldwide. For example, in the United States, sales taxes are a regressive tax policy imposed on the majority of state and local levels. Sales taxes vary by state and locality but generally range from 5% to 7% of the purchase price. Additionally, payroll taxes used to finance Social Security and Medicare are regressive because they are capped at a certain income level. In India, the Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a regressive tax policy imposed at the federal level. The GST is a consumption tax that is levied on goods and services. While the GST has a progressive element because it exempts certain essential goods such as food and medicine, it is still considered regressive because it burdens low-income households more. Regressive tax systems are often compared to progressive and proportional tax systems. While a regressive tax system has some advantages, it also has significant disadvantages compared to progressive and proportional tax systems. When comparing regressive tax systems to progressive and proportional ones, it is essential to consider each tax system's social and economic impact. While a regressive tax system may have some advantages in terms of simplicity and lower administrative costs, it can have a negative impact on low-income households and the overall economy. A progressive tax system, on the other hand, can reduce income inequality, increase social mobility, and stimulate economic growth. A progressive tax system is a tax system in which the tax rate increases as the taxpayer's income increases. It is designed to reduce income inequality and increase social mobility. This tax system can positively impact economic growth by reducing income inequality and increasing consumer spending. A proportional tax system is one in which the tax burden is the same for all income levels. A proportional tax system, such as a flat income tax rate, is often used for flat taxes. While a proportional tax system may seem fair, it can have negative social and economic consequences. For example, a flat income tax rate may place a more significant burden on low-income households, who are already struggling to make ends meet. There are several possible solutions to address the negative impact of a regressive tax system on low-income households and the economy. One potential solution is implementing a progressive tax system that burdens high-income households more. This can reduce income inequality and increase social mobility. A progressive tax system can also stimulate economic growth by increasing consumer spending. Another potential solution is implementing tax policies targeting specific industries or activities. For example, a carbon tax could be implemented to discourage the use of fossil fuels and encourage the use of renewable energy sources. A carbon tax would burden high-income households, which tend to have a higher carbon footprint than low-income households. A regressive tax system can significantly negatively impact low-income households and the economy as a whole, which is why it is important to understand its impact. While it has some advantages in terms of simplicity and lower administrative costs, the disadvantages outweigh the benefits when compared to progressive and proportional tax systems. To address the negative impact of a regressive tax system, implementing a progressive tax system or tax policies targeting specific industries or activities could reduce income inequality, increase social mobility, and stimulate economic growth. Navigating the complexities of tax systems and financial planning can be daunting. That is why hiring a professional tax services provider is crucial to help you make informed decisions about your finances and plan for the future. What Is a Regressive Tax System?
Impact of Regressive Tax System on Low-Income Households
Examples of Regressive Tax Policies and Their Impact
Impact of Regressive Tax System on the Economy
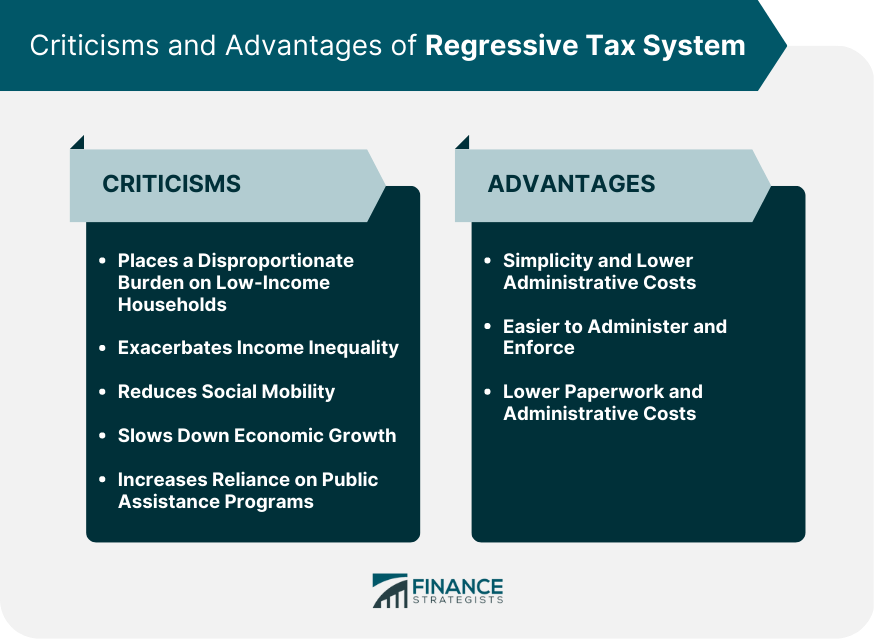
Criticisms of Regressive Tax System
Advantages of Regressive Tax System
Examples of Regressive Tax System
Comparison of Regressive Tax System With Other Tax Systems
Progressive Tax System
Proportional Tax System
Potential Solutions to Address Regressive Tax System
The Bottom Line
Regressive Tax System FAQs
A regressive tax system is one in which the tax burden falls more heavily on low-income and high-income households. The tax rate decreases as the taxpayer's income increases, meaning low-income households pay a higher percentage of their income in taxes than high-income households.
The main disadvantage of a regressive tax system is that it places a disproportionate burden on low-income households, exacerbating income inequality and reducing economic mobility. It can also slow down economic growth by reducing consumer spending.
The main advantage of a regressive tax system is its simplicity and lower administrative costs than a progressive tax system. It requires fewer resources to implement and enforce, resulting in lower costs to the government.
Implementing a progressive tax system or tax policies that target specific industries or activities can address the negative impact of a regressive tax system. These measures can reduce income inequality, increase social mobility, and stimulate economic growth.
Navigating the complexities of tax systems and financial planning can be challenging. A professional tax service provider can help you make informed decisions about your finances and plan for the future, ensuring you understand the impact of a regressive tax system and how to minimize its negative effects.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















